The Future of Energy Storage: Lithium-Ion vs. Solid-State Batteries
2025-03-03
HEXI
In the fast-evolving energy storage industry, two technologies are at the forefront of the conversation: lithium-ion batteries and solid-state batteries. As an international sales professional in the renewable energy battery sector, it’s crucial to understand the strengths, weaknesses, and future outlook of these technologies. A deeper understanding, supported by statistical data, is essential for shaping business strategies and staying competitive in this rapidly changing market.

1. Lithium-Ion Batteries: The Current Market Leader
Lithium-ion batteries have long been the dominant energy storage solution, holding an impressive 85% share of the global battery market as of 2023. They are used extensively in consumer electronics, electric vehicles (EVs), and renewable energy systems due to their well-established performance and scalability. Here are the key advantages:
Performance:
Lithium-ion batteries have a high energy density ranging from 150 to 250 Wh/kg, making them versatile for a broad range of applications. This energy density allows for compact, lightweight batteries that are particularly suited to EVs and portable devices.
Cost Efficiency:
The cost of lithium-ion batteries has experienced a dramatic decline, from around $1,200 per kilowatt-hour (kWh) in 2010 to approximately $137 per kWh in 2023. This price drop can be attributed to significant advancements in battery chemistry, manufacturing processes, and economies of scale. As a result, lithium-ion batteries have become more accessible, driving their widespread use.
Infrastructure Support:
Lithium-ion batteries benefit from a robust existing infrastructure. There are over 2 million public charging stations globally for electric vehicles, with many more being added each year. This established network facilitates the widespread adoption of lithium-ion-powered devices, particularly in the automotive sector.
Challenges:
Despite their advantages, lithium-ion batteries are not without drawbacks. Safety remains a concern, especially with the risk of thermal runaway, where excessive heat causes batteries to catch fire. The frequency of battery fire incidents is around 0.1% of all lithium-ion batteries in use. Additionally, the environmental impact of mining for lithium and cobalt, as well as the challenges surrounding battery disposal and recycling, presents sustainability concerns for both manufacturers and consumers.
2. Solid-State Batteries: The Emerging Contender
Solid-state batteries represent a game-changing technology with the potential to surpass lithium-ion in several key areas. By replacing the liquid electrolyte found in lithium-ion batteries with a solid electrolyte, solid-state batteries are poised to revolutionize the energy storage market. Here are the primary advantages:
Safety:
One of the most significant benefits of solid-state batteries is their superior safety profile. The solid electrolyte reduces the risk of thermal runaway by more than 20 times compared to traditional lithium-ion batteries. This makes them a much safer option for high-risk applications, such as electric vehicles, where battery safety is paramount.
Energy Density:
Solid-state batteries have the potential to achieve much higher energy densities, potentially reaching 500 Wh/kg or more. This translates into longer battery life for electric vehicles (EVs) and greater range for consumer electronics. This increased energy density could revolutionize the range and performance of EVs, solving one of the biggest challenges in the automotive industry.
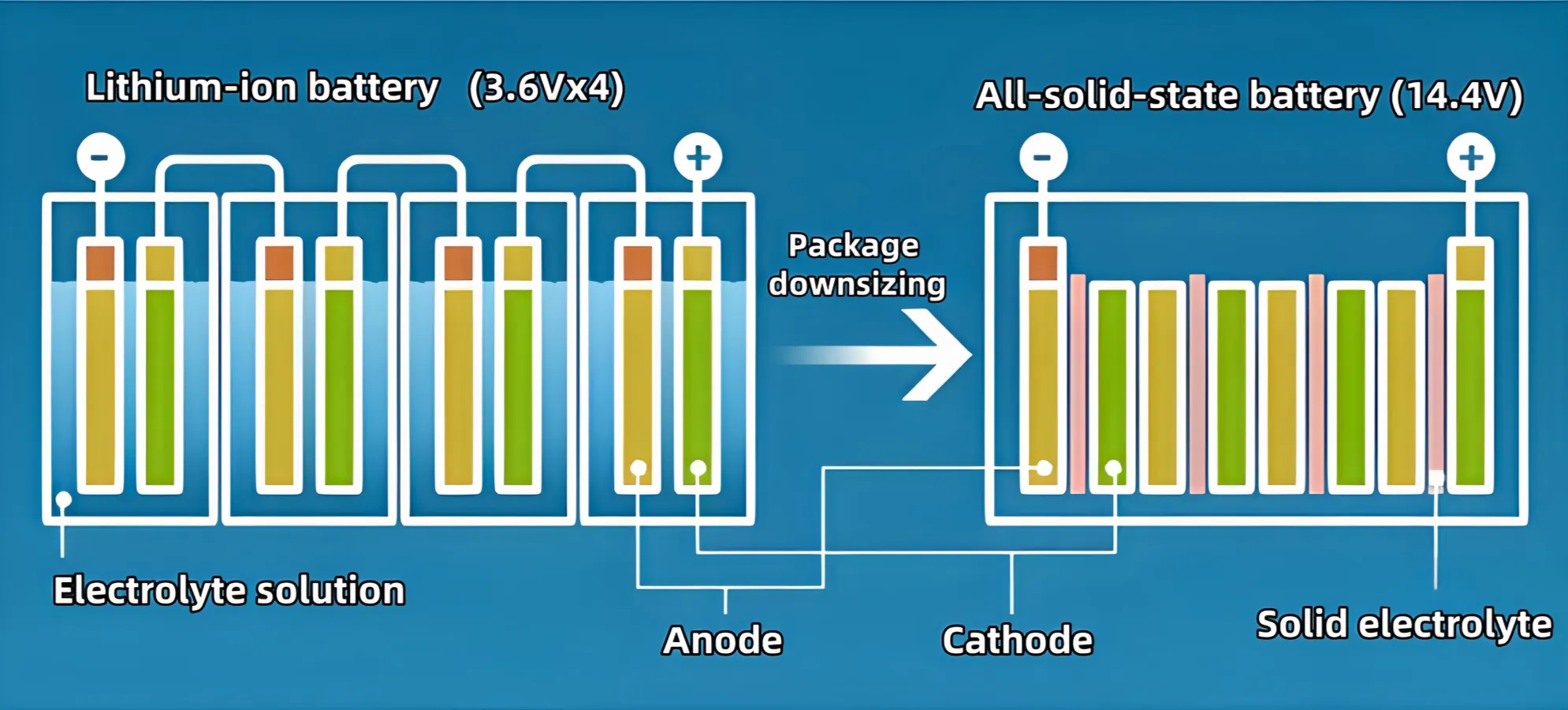
Longevity:
Solid-state batteries could provide up to 2,000 cycles, compared to 500-1,500 cycles for lithium-ion batteries. This significantly longer lifespan makes them more sustainable over time and reduces the need for frequent battery replacements, offering an advantage for long-term applications in renewable energy systems and EVs.
Challenges:
The major hurdle for solid-state batteries lies in production costs. At present, the cost is projected to be around $300 per kWh, which is still considerably higher than lithium-ion batteries. However, technological advancements and large-scale production are expected to reduce these costs significantly in the coming years. Scalability remains an issue, but research and development in this space are advancing rapidly.
3. Market Trends and Future Projections
The battle between lithium-ion and solid-state batteries is intensifying, with several trends driving the competition forward:
Investment in Research & Development (R&D):
The global solid-state battery market is expected to grow from $300 million in 2023 to $7.4 billion by 2028, reflecting a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 62.8%. As manufacturers pour resources into R&D, solid-state battery technology will continue to improve, with cost reductions and performance enhancements expected to accelerate over the next decade.
Consumer Demand for Electric Vehicles:
The demand for electric vehicles (EVs) is set to surge, with global EV sales expected to hit 26 million units by 2030. This growing demand will create intense pressure on battery manufacturers to provide better energy storage solutions that meet the needs of the automotive industry. As EVs require high-performing, long-lasting batteries, solid-state technology may become increasingly attractive as a viable alternative.
Regulatory Support:
Governments around the world are providing strong regulatory support to promote clean energy technologies. For example, the European Union aims to have 30 million zero-emission vehicles on its roads by 2030. This ambitious goal is likely to fuel the adoption of solid-state batteries, which are safer and more energy-efficient than traditional lithium-ion batteries.
A Complementary Future?
While lithium-ion batteries will likely maintain their dominance in the short term, solid-state batteries represent a promising future for energy storage. As the technology matures and production costs decrease, solid-state batteries could capture a significant share of the market, especially in high-demand applications such as EVs and renewable energy systems.
For businesses in the renewable energy sector, staying up-to-date with these advancements is essential. By understanding the strengths, weaknesses, and statistical trends driving these technologies, sales professionals can position their solutions more effectively and stay ahead of the competition. In an increasingly competitive landscape, adaptability and strategic foresight will be key to success as the energy storage market evolves.
This enhanced version provides more detailed insights into both technologies, their market dynamics, and how they relate to each other. It also includes more specific data points, making it a valuable resource for decision-makers and professionals in the renewable energy sector

